Complex Fertiliser
DAP, MAP, NP & NPK
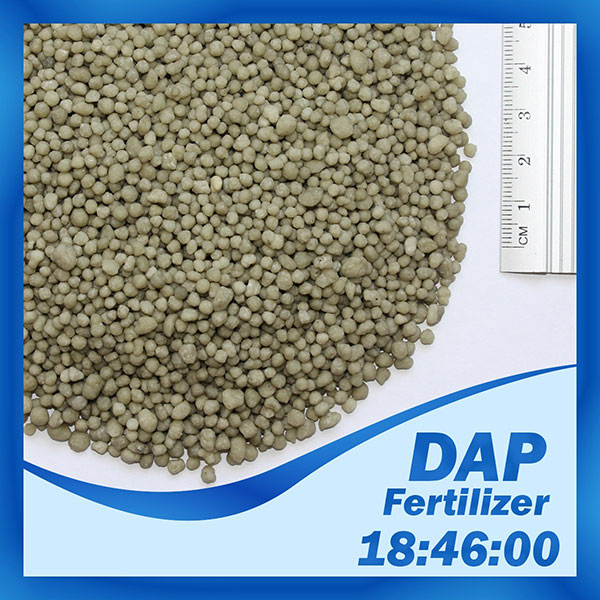
DAP

MAP

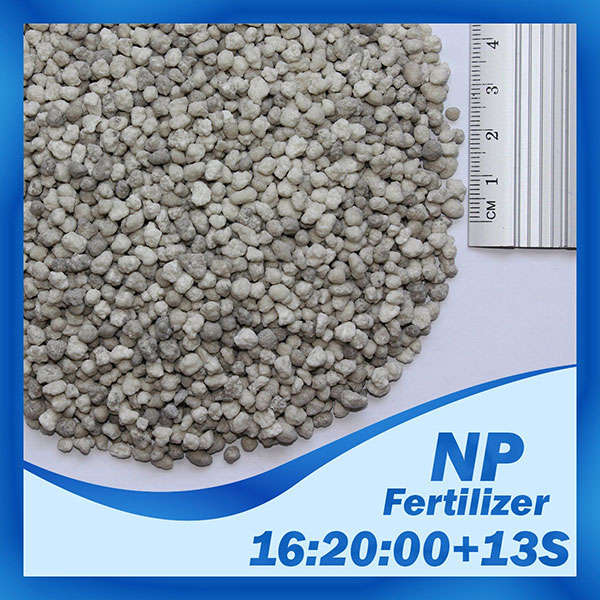
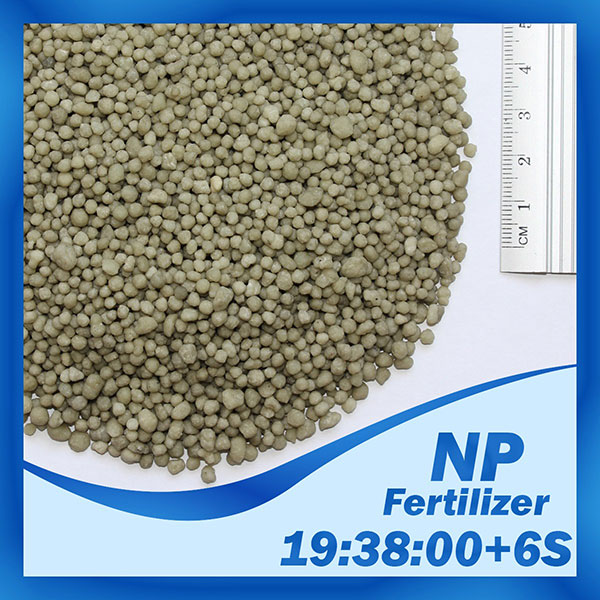
NP

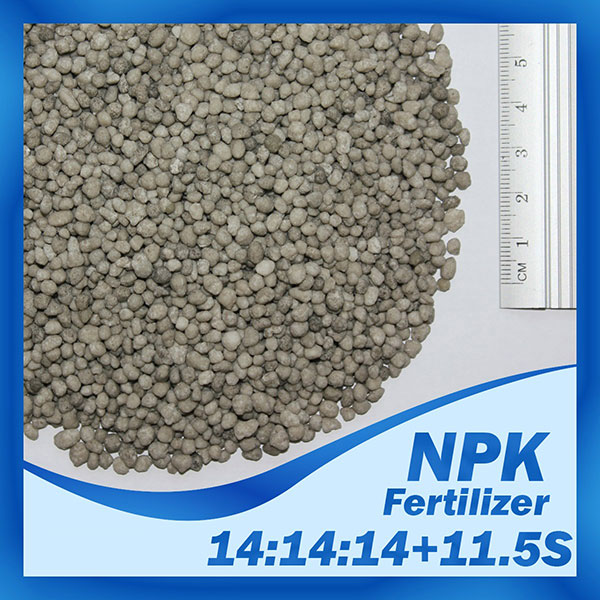
NPK

Fertilizer DAP Introduction:
Chemical Formula: (NH4)2HPO4
Di-ammonium phosphate (DAP 18-46-0) is one of a series of water-soluble ammonium phosphate salts that can be produced when ammonia reacts with phosphoric acid.
Di-ammonium phosphate is a concentrated fertilizer with high phosphorus and nitrogen content. It can be applied directly to soil of as a mixture with other fertilizers.
Physical Form:
Di-ammonium phosphate is a granulated fertilizer, with granules in size 2-4 mm (min. 90%). Granules can be Khaki green, light to dark gray, white, brown, yellow or black (with tones) DAP contains 18% of nitrogen in ammonia form and 46% of phosphorus as ammonium phosphate (exact formula can differ slightly depending on producer).
USES:
• DAP is used as a fertilizer. DAP can be applied for all field crops, grassland and in gardens and orchards. For the best effect DAP should be applied prior to sowing mixed with soil at the depth of ca. 20cm under the ground. It is recommended to use it in early Spring mainly for winter crops. DAP gives optimal effects when applied with potassium chloride which it can be mixed at any time. Directly before spreading it can be also blended with urea, ammonium nitrate and CAN.
• DAP can be used as a fire retardant. It lowers the combustion temperature of the material, decreases maximum weight loss rates, and causes an increase in the production of residue or char. These are important effects in fighting wildfires as lowering the pyrolysis temperature and increasing the amount of char formed reduces that amount of available fuel and can lead to the formation of a firebreak. It is the largest component of some popular commercial firefighting products.
• DAP is also used as a yeast nutrient in winemaking and mead brewing; as an additive in some brands of cigarettes purportedly as a nicotine enhancer; to prevent afterglow in matches, in purifying sugar; as a flux for soldering tin, copper, zinc and brass; and to control precipitation of alkali-soluble and acid-insoluble colloidal dyes on wool.
GRADES:
Binary fertilizer consisting of two elements
Nitrogen and Phosphorus
1. 18-46-00
18-46-00
Fertilizer MAP Introduction:
Chemical Formula: NH4H2PO4
Mono-Ammonium phosphate (MAP 11-52-0) is a widely used source of phosphorus (P) and nitrogen (N). It’s made of two constituents common in the fertilizer industry and contains the most phosphorus of any common solid fertilizer. It’s a lower PH phosphate fertilizer, it’s an excellent dry, and best used for high-alkaline soils. It is an ideal starter fertilizer because MAP contains less ammonia-nitrogen.
Ammonia gas is combined with phosphoric acid, granulated, dried and screened. MAP has been an important phosphate fertilizer for growers around the world for many years. The nitrogen in MAP is in the ammonium form, which resists leaching and is a slower release form of nitrogen. The product has an acid reaction in the soil which can be an advantage in neutral and high pH soils. Therefore, MAP is used in preference to DAP on alkaline soils.
Physical Form:
It is completely water soluble, generally applied in the granular form and used in the formulation of suspension fertilizers. As a granular material, it mixes well and frequently serves as an ingredient in bulk-blended fertilizers.
USES:
One of the major cropping fertilizers used in various countries as a source of phosphorus and nitrogen, MAP and MAP blends are used extensively in cropping systems and for sowing pastures. The low level of nitrogen makes it useful as a ‘starter’ fertilizer and as there is no free ammonia, the risk of affecting germinating seeds is minimal.
Growers apply granular MAP in concentrated bands beneath the soil surface in proximity of growing roots or in surface bands. It’s also commonly applied by spreading it across the field and mixing it into the surface soil via tillage.
It would be used for long term soil building.
GRADES:
Binary fertilizer consisting of two elements
Nitrogen and Phosphorus
1. 11-52-00
11-52-00
Fertilizer NP Introduction:
Chemical Formula: ((NH4)2HPO4 + (NH4)2SO4)
NP is a Binary fertilizer consisting of two elements; Nitrogen and Phosphorus. Major two-component fertilizers provide both nitrogen and phosphorus to the plants. These are called NP fertilizers. The main NP fertilizers are monoammonium phosphate (MAP) and diammonium phosphate (DAP). The active ingredient in MAP is NH4H2PO4. The active ingredient in DAP is (NH4)2HPO4. About 85% of MAP and DAP fertilizers are soluble in water.
GRADES:
Binary fertilizer consisting of two elements
Nitrogen and Phosphorus
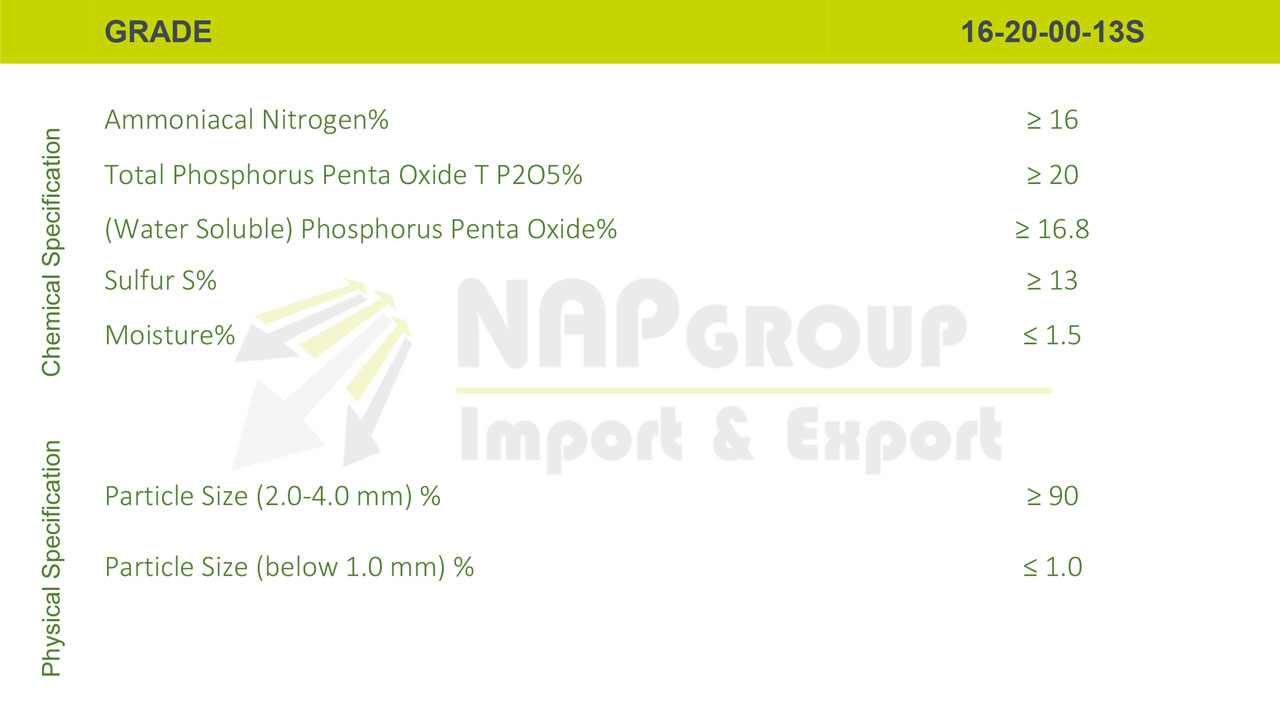
1. 16-20-00+13S
2. 16-20-00+13S+TE
3. 19-38-00+6S
4. 12-46-00+5S
5. 20-20-00+13S
6. 13-40-00+7S
7. 13-40-00+7S+TE
8. 10.4-48-00+4MN
Fertilizer NPK Introduction:
Chemical Formula: (N-P2O5-K2O)
NPK fertilizers are Ternary fertilizer consisting of three elements Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Potassium. Produced by neutralizing of phosphoric and Sulphur acids mixture with ammonia. NPK fertilizer is a complex fertilizer comprised primarily of the three primary nutrients required for healthy plant growth, without any one of which plants could not survive, are referred to as the primary macronutrients:
Nitrogen (N): leaf growth;
Phosphorus (P): Development of roots, flowers, seeds, fruit;
Potassium (K): Strong stem growth, movement of water in plants, promotion of flowering and fruiting;
Physical Form:
NPK is water soluble, 100% friable, non-hygroscopic, with equalized granulometric composition, non-dust forming and practically free of foreign substances. Production form can be in the form of powder and liquid. There may also be a granular structure.
USES:
This fertilizer is valuable for fertilizer blending, and better comparing to MAP, regarding phosphor solubility and high nitrogen concentration. Fertilizer is very effective for spring barley, corn, oilseed rape and sunflower on the soils with low and medium degree of phosphorus moving and sulfur deficiency. These fertilizers can be used dripping and leaves.
GRADES:
Ternary fertilizer consisting of three elements
Nitrogen and Phosphorus and Potassium
1. 14-14-14+11.5S
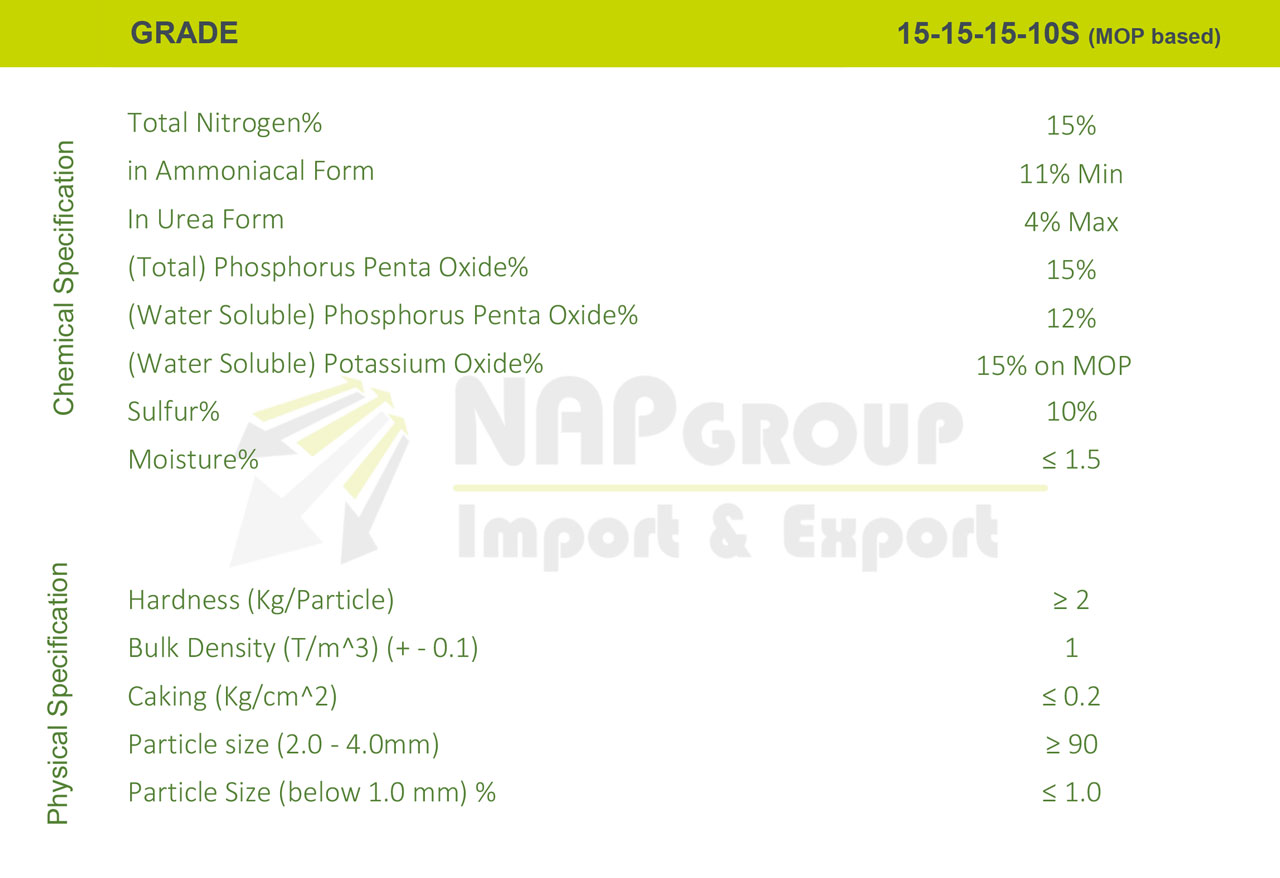
2. 15-15-15+10S
3. 12-30-12
4. 12-30-12+TE
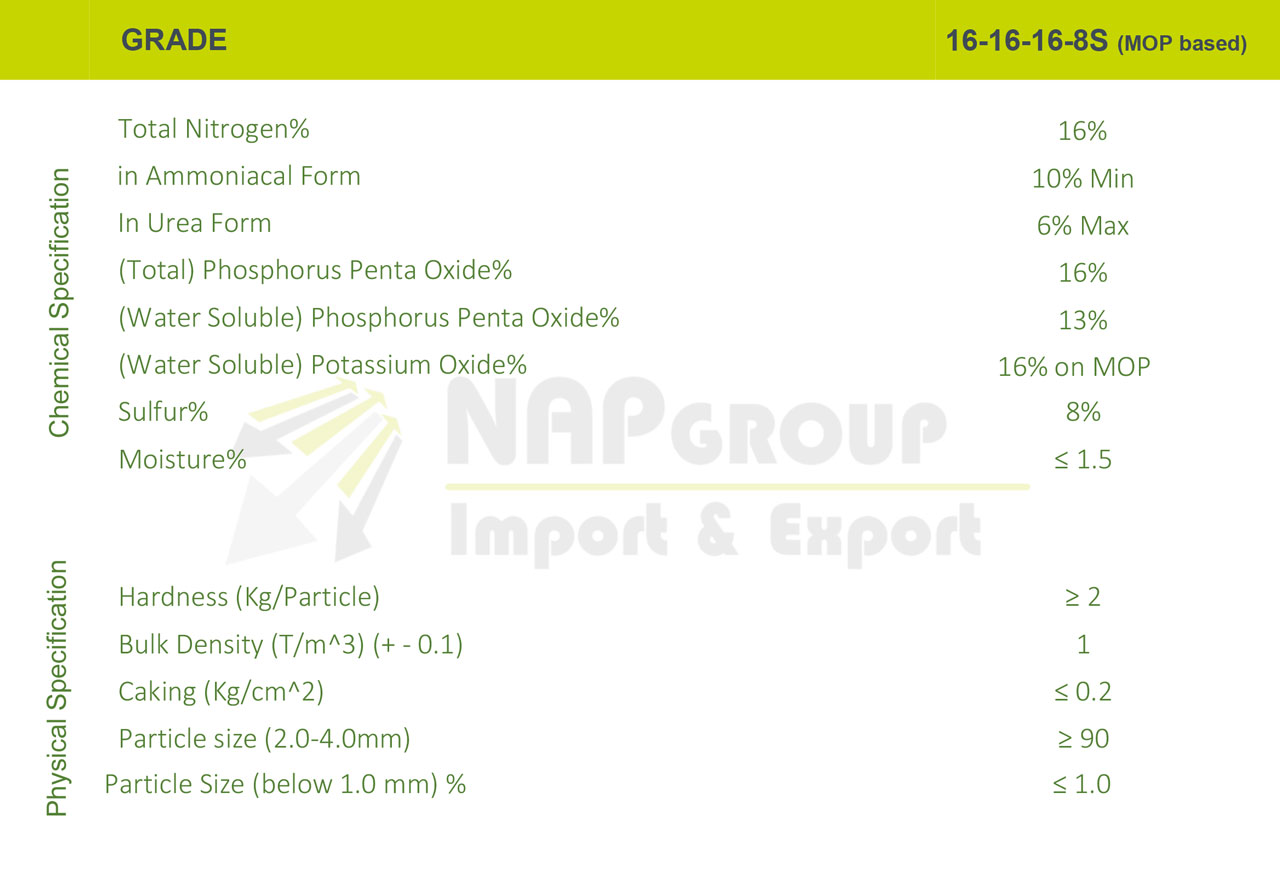
5. 16-16-8+13S
6. 10-28-15+5S
7. 10-28-15+5S+TE
8. 8-16-30
9. 9-24-13+3MgO
10. 10-20-20+7S
11. 10-20-20+7S+TE
12. 10-26-26
13. 12-12-17+2MgO
14. 8-19-28+4S